数据结构
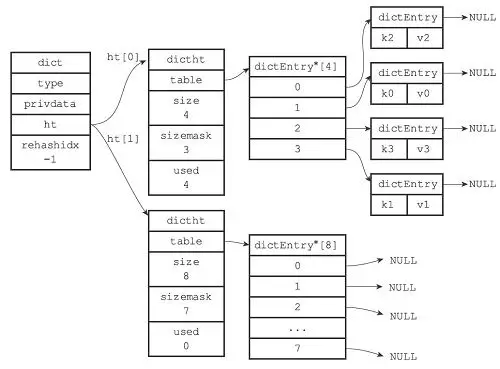
相关源码:
https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/5.0/src/dict.h
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we
* implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;
unsigned long size;
unsigned long sizemask;
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
dictht ht[2];
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */
} dict;
rehash
rehash 的目的在于让哈希表的负载因子 load_factor=ht[0].used/ht[0].size 维持在一个合理范围内。
当出现以下任意情况时,redis 需要对哈希表进行扩容:
- 服务器目前没有在执行 BGSAVE 命令或者 BGREWRITEAOF 命令, 并且哈希表的负载因子大于等于 1。
- 服务器目前正在执行 BGSAVE 命令或者 BGREWRITEAOF 命令, 并且哈希表的负载因子大于等于 5 。
根据 BGSAVE 命令或 BGREWRITEAOF 命令是否正在执行, 服务器执行扩展操作所需的负载因子并不相同, 这是因为在执行 BGSAVE命令或 BGREWRITEAOF 命令的过程中, Redis 需要创建当前服务器进程的子进程, 而大多数操作系统都采用写时复制(copy-on-write)技术来优化子进程的使用效率, 所以在子进程存在期间, 服务器会提高执行扩展操作所需的负载因子, 从而尽可能地避免在子进程存在期间进行哈希表扩展操作, 这可以避免不必要的内存写入操作, 最大限度地节约内存。
当出现以下情况时,redis需要对哈希表进行缩减:
- 负载因子小于0.1,此时空间浪费比较严重。
当哈希表的键值对数量过多或过少时,需要对哈希表大小扩展或收缩,这样的工作需要 rehash 来完成。
dictht ht[2]; ,dict 中维护着两个哈希表,即为了rehash 用。
假设哈希表 ht[0] 的 used (实际包含的键值对数量)为 n,当 hash 需要扩容或缩减时,将 ht[1] 的大小扩到或缩小到最小的 \(n \times {2^m}\) 。然后将 ht[0] 键值对重新计算哈希值和索引值逐步移到 h[1] 中。 当 ht[0] 中的所有键值对清空后,释放 ht[0],将 ht[1] 设为 ht[0],然后在新建一个 ht[1]。
rehashidx 表示了ht[0] 键值对迁移到ht[1] 的状态:
- 为0时,表示 rehash 正式开始。
- 当 rehash 完成一次,rehashidx 加1。
- 当 ht[0] 所有键值对 rehash 到 ht[1] 后,rehashidx 置为 -1。
内部编码
ziplist
压缩列表。使用这种编码有2个条件:
- 元素个数小于
hash-max-ziplist-entried,默认为512 - 所有值均小于
hash-max-ziplist-value,默认64字节
ziplist 结构更紧凑,存储连续,相较于 hashtable 更加节约内存。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
127.0.0.1:6379> hmset demo k1 apple k2 huawei
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> hgetall demo
1) "k1"
2) "apple"
3) "k2"
4) "huawei"
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding demo
"ziplist"
hashtable
哈希表。当数据无法满足 ziplist 的条件时,若使用 ziplist 实现,读写效率会下降,因此使用 hashtable 实现,但 hashtable 消耗更多内存。hashtable 读写时间复杂度为 \(O(1)\)。
1
2
3
4
127.0.0.1:6379> hset demo k3 "this value is more than 64 bytes:abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLIMOPQRSTUVWXYZ"
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding demo
"hashtable"
常用命令
对 field 的操作
| 命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| hdel key {field} | 删除 field |
| hexists key f{ield} | 检查 field 是否存在 |
| hget key {field} | 获取 field 值 |
| hstrlen key {field} | 获取 field 值长度 |
| hset key {field} {value} | 给 field 设置值 |
| hsetnx key {field} {value} | 如果 field 不存在的话设置值,即只创建不更新 |
| hincreby key {field} {increment} | 给 field 的值自增整型值 |
| hincrebyfloat key {field} {increment} | 给 field 的值自增浮点值 |
对整体的操作
| 命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| hgetall key | 获取所有 field 和 value |
| hkeys key | 获取所有 field |
| hmget key field [field2 field3…] | 批量获取 field 的值 |
| hmset key field value [field2 value2…] | 批量设置 field 和 value |
| hvals key | 获取所有的 value |
| hscan key cursor [match pattern] | 迭代遍历 field 和 value |
| hlen key | 获取hash 的长度(所有 field 的数量) |